👉 NEET Biology Examination
👉 NEET Biology Tips
👉 NEET Biology Study Material
👉 UGC Net Study Material
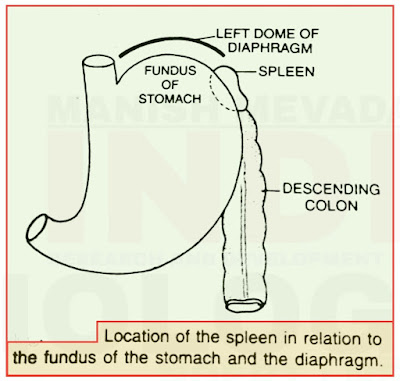
Spleen
- It lies in between the fundus of the stom ach and the diaphragm.
- The spleen is soft, highly vascular and dark purple in colour.
- The spleen is the largest single mass of lymphatic tissue in the body.
- Its average weight in the adult is about 150 gm.
- Its long axis lies in the line of the tenth rib.
Structure
- The spleen has a long fissure, the hilium, near its lower portion.
- Except at the hilum, the surface of the spleen is covered by a layer of visceral peri toneum ( = serous coat ).
- Next to the visceral peritoneum, there is a capsule.
- The trabecu- lae arise from the capsule that extend into the substance of the spleen.
- White Pulp
- The lymphoid tissue (mostly lymphocytes) surround the arterioles, form ing masses or nodules, the splenic nodules (= Malpighian bodies) which appear whitish and hence called the white pulp of the spleen.
- Red Pulp . The remaining part of the splenic tissue appears reddish due to red blood corpuscles and hence, called the red pulp of spleen.
- It contains numerous venous sinu soids which are large and complex cavities containing blood.
- The venous sinusoids are separated by areas of tissue rich in macroph ages attached to the reticulum of the spleen called Splenic cords of Billroth.
- The term 'cord' is perhaps misleading, because these areas of perivascular tissue form a continu ous network throughout the spleen and have numerous cavities between the cells through which blood can pass.
- In some mammals like mouse and cat, there are no sinusoids and the majority of the red pulp is composed of splenic cord tissue.
- Blood circulation in the spleen is as follows : Splenic artery→Arterioles → Venous sinusoids → Venules → Splenic vein.
- Phagocytosis. The splenic macrophages engulf worn - out red blood corpuscles , white blood corpuscles and platelets and cell debris and microorganisms
- Haemopoiesis. In foetus , the spleen produces all types of blood cells but in adult it only produces lymphocytes
- Immune response. Like other lymphoid tissues, the spleen is a centre where both B - lymphocytes and T - lymphocytes multiply.
- When stimulated by the presence of antigen, the B - lymphocytes enlarge and get converted to plasma cells.
- The plasma cells produce antibodies, the protective proteins that provide immunity.
- T - lymphocytes are also concerned with immune responses.
- They can destroy abnormal cells by direct contact or by producing cytotoxic substances called cytokines.
- Storage of Erythrocytes. When the animal needs less oxygen, some erythrocytes ( RBCs ) are withdrawn from the blood circulation and stored in the spleen.
- When the animal requires more oxygen the stored erythrocytes are released into the blood circulation, there fore, spleen is often called “ Blood bank ".
- The enlargement of the spleen is called splenomegaly.
- It happens during the following coditions,
- Increased phagocytosis by macrophages as in any infection.
- Increased destruction of erythrocytes as in malaria
- Abnormal increase in lymphocyte production as in leukaemia-blood cancer.
========================================
Mail- indiabiologymanishmevada@gmail.com







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box