👉 NEET Biology Examination
👉 NEET Biology Tips
👉 NEET Biology Study Material
👉 UGC Net Study Material
Cardiac Output
- Cardiac Output (Heart Output) The amount of blood pumped by heart per minute is called cardiac output or heart output.
- Heart of a normal person beats 72 times per minute and pumps out about 70 mL of blood per beat.
- Thus the cardiac output is 72 x 70 or 5040 mL per minute i.e., about 5 litres per minute which is equivalent to the total body blood volume (about 5.5 litres).
Pulse
- Pulse is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main arteries.
- Thus pulse is a wave of increase which passes through arteries as the left ventricle pumps its blood into the aorta.
- Pulse is a regular jerk of an artery. Therefore, it is also called arterial puls.
- The pulse rate is exactly the same as the heart rate because an artery pulses every time the heart beats.
- Pulse is usually taken on the radial artery in the wrist but it can be taken on any artery that flows near enough to the surface of the body to be felt.
- The factors which affect the pulse rate are as follows :
- The pulse rate in children is more rapid than in adults.
- The pulse rate is more rapid in the female than in the male.
- When the person is standing up the pulse rate is more rapid than when he/she is lying down.
- When any strong emotion is experienced the pulse rate is increased, for example, anger, excitement, fear, etc.
- Any exercise increases the rate of the pulse.
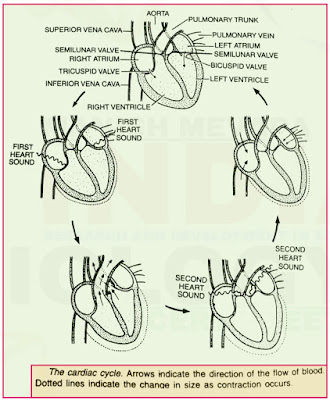
Cardiac Cycle
- The cardiac cycle consists of one heart beat or one cycle of contraction and relaxation of the car diac muscle.
- During a heart beat there is contraction and relaxation of atria and ventricles.
- The contraction phase is called the systole while the relaxation phase is called the diastole.
- When both the atria and ventricles are in diastolic or relaxed phase this is referred to as a joint diastole.
- During this phase, the blood flows from the superior and inferior venae cavae into the atria and from the atria to the respec tive ventricles through auriculo ventricular valves.
- But there is no flow of blood from the ventricles to the aorta and pulmonary trunk as the semilunar valves remain closed.
- The successive stages of the cardiac cycle are briefly described below.
- Atrial Systole.The atria contract due to a wave of contraction , stimulated by the SA node. The blood is forced into the ventricles as the bicuspid and tricuspid valves are open .
- Beginning of Ventricular Systole. The ventricles begin to contract due to a wave of contraction , stimulated by the AV node . The bicuspid and tricuspid valves close immedi ately producing part of the first heart sound.
- Complete Ventricular Systole. When the ventricles complete their contraction , the blood flows into the pulmonary trunk and aorta as the semilunar valves open.
- Beginning of Ventricular diastole. The ventricles relax and the semilunar valves are closed . This causes the second heart sound.
- Complete Ventricular Diastole The tricuspid and bicuspid valves open when the pressure in the ventricles falls and blood flows from the atria into the ventricles . Contraction of the heart does not cause this blood flow . It is due to the fact that the pressure within the relaxed ventricles is less than that in the atria and veins.
- The duration of a cardiac cycle is 0.8 sec .
========================================
Mail- indiabiologymanishmevada@gmail.com







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box