👉 NEET Biology Examination
👉 NEET Biology Tips
👉 NEET Biology Study Material
👉 UGC Net Study Material
Blood Groups
- There are more than 30 antigens on the surface of blood cells that give rise to different blood groups.
- In a blood transfusion, certain blood groups, e.g. , ABO blood group, of the recipient and donor must be matched, otherwise the recipient's immune system will produce antibodies that cause agglutination of the transfused cells and block blood circulation through capillaries.
- Two types of blood groups - ABO Blood Group and Rh Blood Group (Rh Factor) are widely used all over the world.
ABO Blood Groups
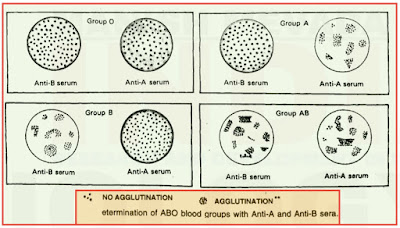
- Karl Landsteiner reported first time ABO blood groups in human beings.
- A , B and O blood groups were discovered by Landsteiner (1900) while AB blood group was found out by de Castello and Steini (1902).
- ABO blood groups are determined by the gene 1 (isoagglutinogen).
- There are three alleles, IA , IB and Io of this gene.
- Proteins produced by the A and B alleles are called A antigen and B antigen.
- People with blood group A have the A antigen on the surface of their RBCs, and antibodies to antigen B in their plasma.
- Persons with blood group B have B antigen on their RBCs, and antibodies against A antigen in their plasma.
- Individuals with AB blood group have both antigen A and antigen B on their RBCs , and no antibodies for either of the antigens in their plasma.
- Type O individuals are without A and B antigens on their RBCs, but have antibodies for both these antigens in their plasma.
- Individuals with blood group AB can receive blood of A , B or O group, while those with blood group O can donate blood to anyone.
- This is the most important blood group for transfusion.
- Thus person with blood group AB is called universal recipient and person with blood group O is called universal donor.
- If a blood transfusion is made between an incom patible donor and recipient , reaction of antigens on the cells and antibodies in the plasma produces clots that clog capillaries.
Rh (Rhesus) Blood Group.
- A protein named as rhesus antigen, is present on the surface of red blood corpuscles in many persons.
- It was discovered in 1940 by Landsteiner and Wiener in the blood of Rhesus monkey, hence its name.
- Depending on the race 85 to 99 percent of the white population have this rhesus antigen (also called Rh factor) and are called Rh positive (Rh +).
- Others who do not have this factor are known as Rh negative (Rh).
- Rh is dominant to Rh- . Whites Rh + 85 % , Rh- 15 %, American Blacks Rh 95 %, Rh 5 %, African Blacks Rh + 100 %.
- Formation of Rh protein is controlled by a dominant gene which may be called as R.
- Thus , RR (homozygous) and Rr (heterozygous) persons are dominant and are Rh positive and rr (homozygous) are recessive and are Rh- negative.
- Both Rht and Rh individuals are phenotypically normal.
- The problem arises during blood transfusion and pregnancy.
- Incompatibility during Blood Transfusion
- The first blood transfusion of Rh+ blood to the person with Rh- blood causes no harm because the Rh- person develops anti Rh factors or antibodies in his / her blood.
- In second blood transfusion of Rht blood to the Rh person, the latter's anti Rh factors attack and destroy the red blood corpuscles of the donor.
- Incompatiblity during Pregnancy
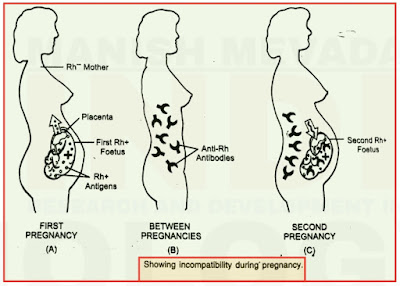
- If father's blood is Rh+ and mother's blood is Rh- , the foetus' (baby in the uterus) blood is Rh+.
- This is a serious problem.
- If the Rh- blood of mother has not earlier come in contact with Rh+ blood through transfusion, her first child does not suffer (although the Rh blood of the foetus stimulates the formation of anti Rh factors or antibodies in the mother's blood yet enough anti Rh factors are not produced in the mother's blood to harm the foetus).
- But in the subsequent Rh+ foetuses, the anti Rh factors (antibodies) of the mother' blood destroy the foetal red blood corpuscles.
- This results in haemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
- It is called erythroblastosis foetalis (destruction of the erythrocytes of foetus).
- Newbom may survive but it is often anaemic In order to prevent HDN, Rh- mothers are injected with a defective anti Rh- antibody during all pregnancies carrying Rh+ foetus.
- Marriage between Rh- woman and Rh+ man is not recommended. Rh+ is dominant .
========================================







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box