Bioreactors (Fermenters)
- Bioreactors are considered as ves sels in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products by microbes, plant and animal cells and / or their enzymes.
- Small volume cultures cannot give large quantities of the products .
- Large scale production (100 - 1000 litres) of the products is carried out in bioreactors.
- A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for obtaining the de sired product by providing opti mum growth conditions such as temperature, pH, substrate, vitamins, oxygen and salts.
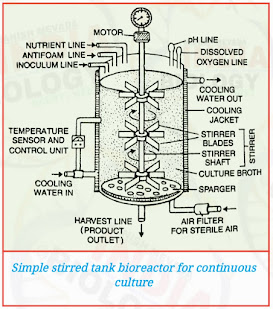
- The most commonly used bioreactors are of stirring type.
- Stirring type bioreactors are
- Simple stirred - tank bioreactor and Sparged stirred - tank bioreactor
- In the sparged stirred - tank bioreactor, sterile air bubbles are sparged.
- The surface area for oxygen transfer is increased.
- Fermentation is the process by which microor ganisms turn raw material such as glucose into products such as alcohol.
- The term fermentations originally applied only to anaerobic processes but is now used more broadly to include all processes whether aerobic or anaerobic.
- All operations are carried out under sterile conditions to avoid contamina tion of the culture.
- The product is either the cells themselves (biomass) or some useful cell product.
- Two basic types of fermentation are possible.
- These are batch fermenta tion and continuous fermentation.
- In batch fermentation, the nutrients and microorganisms are put in a closed reactor and not changed from outside once the fermentation starts, for example, no more nutrients are added.
- When nutrients are utilized, the product is separated from microorganisms.
- In continuous fermentation nutrients are replaced as fast as they are used and products are removed as fast as they are made.
- The stirred - tank bioreactor is well suited for large - scale production of micro - organisms under aseptic conditions for a number of days.
- It can be used easily in research laboratories Other advantages are an oxygen delivery system, foam control system, a temperature control system, pH control system, etc.
- Drawbacks in this bioreactor are that it is relatively expensive to run it.
- After the formation of the product in the bioreactors, it undergoes through some processes before a finished product to be ready for marketing.
- The processes include separation and purification of products which are collectively called the downstream processing.
- The product is subjected to quality control testing and kept in suitable preservation.
- If drugs are to be manufactured such formulation has to undergo throu clinical trials.
- A proper quality control testing for each product is also needed.
- The downstream processing and quality control test are different from product to product.
========================================







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box