STD-11 UNIT-3 CHA-8
CELL : STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
Prokaryotic Cells - Structure
Prokaryotic Cells or Bacterial cell
- It is a primitive type of cell in which genetic material is not organised in the form of nucleus but instead lies freely in a naked super - coiled state in the cytoplasm whence it is known as prochromosome or nucleiod .
- Prokaryotic ( = procaryotic ) cells are known for their rapid multiplication
- In shape , bacterial cells are of many types.
- Coccus ( Gk . kokkos- berry ) . Coccus bacteria are spherical. ( i ) Monococcus ( occurring singly ) ,( ii ) Diplococus ( in Iwos ) . ( iii ) Tetracoccus ( in tetrads ) . ( iv ) Streptococcus ( in chains ) . ( v ) Staphylococcus ( irregular grape - like clusters ) and ( vi ) Sarcina ( 3 dimensional geo metrical forms ) .
- Bacillus ( L. bacillus small rod ) . The bacterium is straight and cylindrical like a rod with ends being flat rounded or cigar shaped . It has three special types : ( i ) Diplobacillus ( in twos ) . ( ii ) Palisade Bacillus (like a stack ) and ( iii ) Streptobacil lus in chains ) .
- Spirillum ( L. spira coil ) . The bacterium is coiled like a cork - screw , e.g. , Spir illum , Spirochaete . Aggregation does not occur .
- Vibrio . The body of the bacterium is like a comma , curved rod or single turn of the spiral e.g. , Vibrio cholerae . Like spirillum bacteria , the vibrio forms live singly .
- Stalked . The bacterium possesses a stalk , e.g. , Caulobacter .
- Budding . The bacterium is swollen at places , e.g. , Rhodomicrobium .
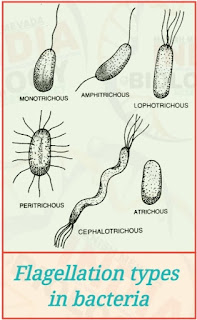
- Depending upon the presence or absence of flagella , bacteria are grouped into flagellate and nonflagellate types . The various forms of flagellation are as follows :
- Atrichous . Flagella absent .
- Monotrichous . A single Nagellum occurs at or near one end of bacterium.
- Amphitrichous . A flagellum at each of the two ends .
- Lophotrichous . A group or tuft of fla gella is found only at one end .
- Cephalotrichous . A tuft or group of flagella occurs at each of the two ends or poles The term amphitrichous is also used for this condition .
- Peritrichous . A number of flagella are distributed all over the surface.
- A bacterial cell consists of a cell envelope , cytoplasm , nucleiod , plasmids . inclusion bodies , flagella , pili and fimbriae .
- It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell . Cell envelope consists of 3 components , glycocalyx , cell wall and cell membrane .
- Glycocalyx .
- It lies outside the cell wall .
- Glycocalyx consists of two parts , inner S - layer and outer mucilage .
- S - layer is mostly made of polypeptides rich in acidic amino acids . Mucilage is carbohydrate rich which when thick is called capsule .
- Glycocalyx gives sticky character to the cell . It is not absolutely essential for survival of bacteria .
- However , it has several secondary functions .
- ( a ) Prevention of desiccation .
- ( b ) Protection from phagocytes .
- ( c ) Protection from toxic chemicals and drugs .
- ( d ) Protection from viruses .
- ( e ) Attachment .
- ( f )Immunogenicity
- ( g ) Virulence .
- Cell Wall .
- It is rigid solid covering which provides shape and structural supportto the cell . Cell wall lies between plasma membrane and glycocalyx . Periplasmic space occurs between plasma membrane and cell wall . Cell wall protects the bacterial cells against bursting in hypotonic solution .
- It is single layered and smooth .
- In Gram negative bacteria ,complex ,wavy and two layered .
- The outer layer is also called outer membrane .
- It consists of lipopolysaccha rides , lipids and proteins . The outer membrane has barrel proteins called porins .
- The single layered cell wall of Gram positive bacteria and inner wall layer of Gram negative is made up of pepidoglycan , proteins , non - cellulosic carbohydrates , lipids , amino acids , etc.
- Peptidoglycan forms the structural network of the cell wall . It is also known as murein or mucopeptide .
- Peptidoglycan consists of long glycan strands formed of repeating units of N - acetyl glucosamine ( NAG ) and N - acetyl muramic acid ( NAM ) .
- Amino acid present in the wall is diaminopimelic acid or lysine .
- In Gram positive bacteria , the wall contains teichoic acids that form receptor sites and surface antigens .
- Plasma Membrane .
- Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane is sermi - permeable in nature and interacts with the outside world.
- This membrane is similar structurally to that of the eukaryotes.
- A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed by the extensions of the plasma membrane into the cell.
- These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
- They help in cell wall formation, DNA replication and distribution to daughter cells.
- They also help in respiration, secretion processes to increase the surlace area of the plasma membrane and enzymatic content.
- In some prokaryotes like cyanobacteria, there are other membranous extensions into the cytoplasm called chromatophores which contain pigments.
- Bacterial cells may be motile or non-motile.
- If motile, they have thin filamentous extensions from their cell wall called flagella.
- Bacteria show a range in the number and arrangement of flagella.
- Bacterial flagellum is composed of three parts - filament, hook and basal body
- filament. The filament is the longest portion and extends from the cell surface to the outside.
- Besides flagella, pili and fimbriae are also surface structures of the bacteria but do not play a role in motility.
- Pili. The pill are elongated tubular structures made of a special protein.
- Fimbriae. The fimbriae are small bristle like fibers sprouting out of the cell. In some bacteria, they are known to help attach the bacteria to rocks in streams and also to the host tissues.
- In prokaryotes ribosomes are associated with the plasma membrane of the cell.
- They are about 15 nm by 20 nm in size and are made of two subunits - 50S and 305 units which when present together form 70S prokaryotic ribosomes.
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
- Several ribosomes may attach to a single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysome.
- The ribosomes of a polysome translate the mRNA into proleins
- Inclusion bodies.
- Reserve materials in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.
- These are not bound by any membrane system and lie free in the cytoplasm, e.g. phosphate granules, cyanophycean granules and glycogen granules.
- Gas Vacuoles are found in blue green and purple and green photosynthetic bacteria.
=======================================================







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box