STD-12 UNIT-6 CHA-2
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANT
DOUBLE FERTILIZATION | ARTIFICIAL HYBRIDISATION
DOUBLE FERTILIZATION
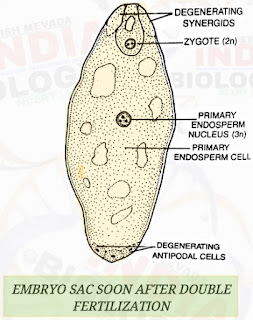
- Double fertilization is the fusion of two male ga metes brought by a pollen tube to two different cells of the same female gametophyte in order to produce two different structures .
- It is found only in angiosperms where it was first discovered by Nawaschin in 1898 in Fritillaria and Lilium .
- In angiosperms the pollen tube bursts open in one of the two synergids to release the two male gametes .
- One male gamete fuses with the egg or oosphere to form a diploid zygote or cospore.It is called generative fertilization .
- The second male gamete descends down and fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus of the central cell to form a triploid primary endosperm cell . It is known as vegetative fertilization .
- In angiosperms the growth of the female gametophyte or embryo sac stops at the 8 - nucleate or 7 - celled stage .
- The second act of fertilization , called vegetative fertilization , provides a stimulus to one of its cells to resume growth and form a nutritive tissue .
- Double fertilization ensures that the nutritive tissue is formed only when the form of embryo has taken place by fertilization of the oosphere or egg. Angiosperms are Therefore, economical and more specialized as compared to gymnosperms where a large nutritive female gametophyte is formed long before fertilization. If fertilization fails, the energy spent on forming it shall go to waste.
- Double fertilization provides the characteristics of the male plant as well as the nutritive tissue.
- Due to its triploid nature, endosperm shows high physiological activity, groids faster and accumulates nutrients.
- It is human performed crossing of two different plants having complementary good traits in order to obtain an overall superior variety.
- Artificial hybridization has been used by plant breeders for crop improvement program even before the days of Mendel.
- Two precautionary measures in artificial hybridization are emasculation and bagging.
- Emasculation is removal of stamens from the floral buds of female parent so that chances of self pollination are eliminated.
- Bagging is the covering of flowers by butter paper or polythene.
- The Emasculation floral buds of the female parents and the floral buds of the male parents are bagged in order to protect them from contamination.
- Pollen grains of the male parents are collected as their anthers mature.
- As the stigmas of the emasculated flowers of the female parents mature, the covering bags are removed one by one for dusting their stigmas with pollen grains of desired variety.
- After pollination, the flowers are rebagged till the fruits begin to ripen.
- The latter will contain seeds of hybrid variety.
- A number of crosses may be required for obtaining the desired variety.
- Emasculation is not required if the flowers are unisexual. However, both the type of flowers must be kept covered by bags.
- This protects them from contamination by unwanted pollen grains







Please do not enter any spam link or word in the comment box